Authors: Wei Chen, Jiachen Zou, Xuming Ran, Dietmar Heinke, Quanying Liu
Date: May 17, 2023
Supervisor: Professor Quanying Liu
Introduction
Scientific Questions:
- Investigating the relationship between visual perception and human decision-making tasks, with a particular focus on the importance of visual semantic features and how these features help us understand the attributes and characteristics of objects.
- Explaining the impact of visual perception on behavioral decisions, exploring the role of visual semantic features in cognitive decision-making processes in humans and AI agents.
Research Methods:
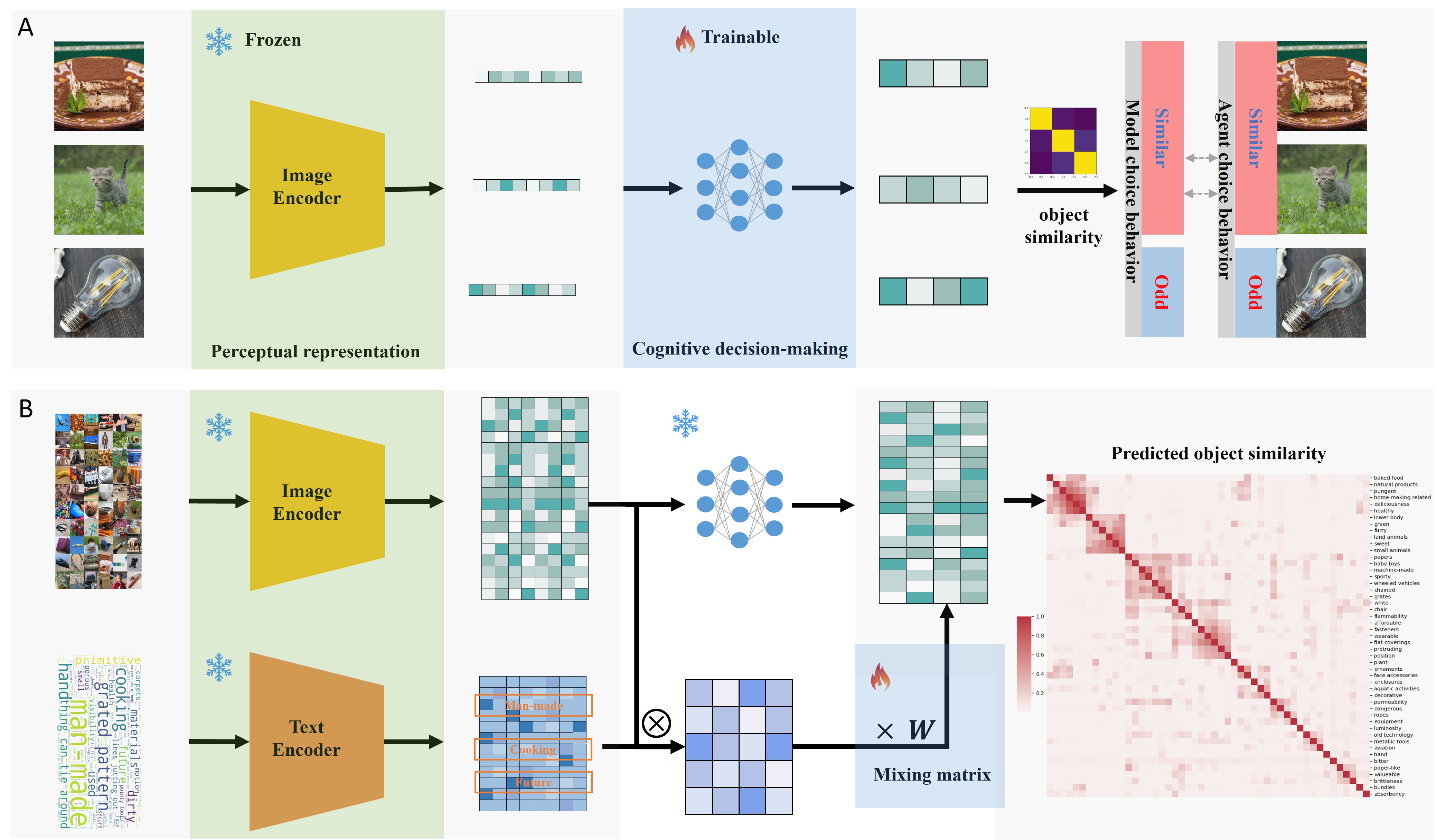
- We introduced a computational model named Multimodal Interpretable Semantic Embeddings (MISE), which employs a model built on the CLIP model and linear mapping functions to simulate the process of visual perception and cognitive decision-making, performing similarity judgment tasks.
- The MISE model utilizes pre-trained visual encoders to extract visual features, and through a learnable cognitive decision module, calculates the similarity between features to make decisions, revealing the semantic properties of visual features within the model.

Method
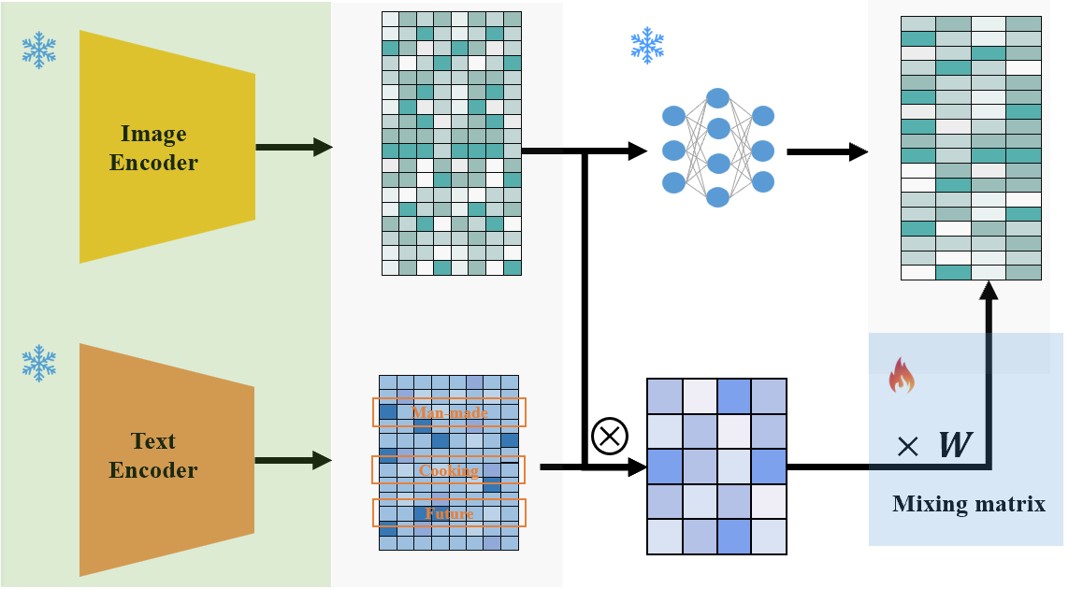
Dataset Selection: Utilizes the THINGS dataset as the human behavior dataset, which contains similarity judgment data for different combinations of visual objects. Generates AI agent behavior dataset by performing similarity judgment tasks using the CLIP model; collects and establishes a lexicon of visual feature descriptors.
MISE Model Construction: Constructs the MISE model based on visual encoders and decision modules, simulating the process from visual stimulation to cognitive decision-making.
Interpretability Validation: Visualizes the interpretation of semantic features by the MISE model to verify its explanatory capability.
Results
MISE Model Accuracy in Behavioral Prediction Tasks: Compares the accuracy of the MISE model in behavioral prediction tasks against random guessing and the upper limit of human decision-making noise, validating the superiority of the MISE model. The MISE model demonstrates stable performance across various model variants and training methods, and is capable of accurately making decisions on unseen image triplets.
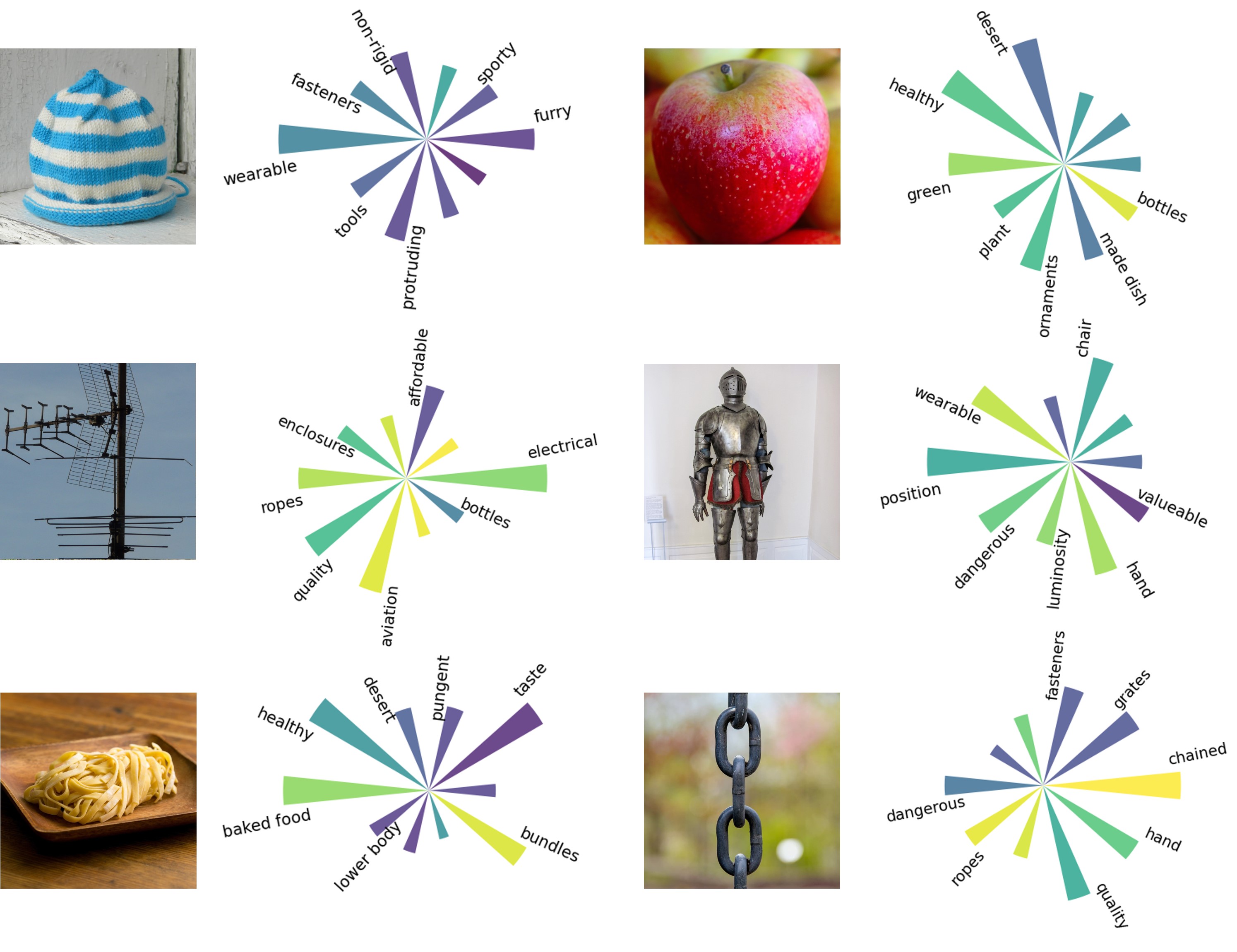
MISE Model’s Interpretability of Semantic Features: Demonstrates the model’s interpretation of semantic features through word clouds and bar charts. The MISE model is capable of interpreting semantic features, providing a deep understanding of the features.

Conclusion
MISE Model Performance in Similarity Tasks: The MISE model shows excellent performance in similarity tasks, capable of making accurate decisions and generating reasonable and diverse explanations, thus validating the effectiveness of the model.
Interpretability Analysis of Semantic Features in MISE Model: Through the interpretative analysis of semantic features in the MISE model, we have generated word clouds and bar charts to display the model’s interpretation and representation of semantic features. This further enhances our understanding of how the model interprets and represents objects, thereby validating the model’s interpretability.
Capturing Key Semantic Features in Visual Stimuli with the MISE Model: The MISE model is able to capture key semantic features in visual stimuli, which are crucial for understanding and distinguishing different objects. By establishing a linear mapping relationship between visual features and semantic properties, we reveal the association between semantic attributes of visual stimuli and perceptual features. This helps to deepen the understanding of the relationship between visual perception and cognitive decision-making.

For more detailed information, see the full paper here: MISE Paper.